高级 RAG:查询扩展
扩展关键词查询以提高召回率并为RAG提供更多上下文。
2024年8月14日这是 **高级用例** 系列的第一部分
1️⃣ 从查询中提取元数据以改进检索
2️⃣ 查询扩展
3️⃣ 查询分解
4️⃣ 自动化元数据丰富
RAG(检索增强生成)的质量高度依赖于过程的第一步:检索的质量。生成步骤只能与它所处理的上下文一样好,而它将作为检索步骤的结果接收。
然而,检索又依赖于它接收到的查询。检索有多种类型:基于关键字、基于语义搜索(嵌入)、混合检索,甚至在某些情况下,仅仅基于查询API的结果(例如,网络搜索结果等)。但归根结底,在大多数情况下,键盘后面都有一个人在输入查询,而人类不能保证生成高质量的查询以获得他们想要的结果。
在本文中,我们将引导您了解一种非常简单但有效的方法,该方法可以确保我们检索到更多、更相关的给定查询的上下文:查询扩展。
TL;DR:查询扩展增加了结果的数量,因此它提高了召回率(相对于精确率)。一般来说,BM25倾向于精确率,而嵌入检索倾向于召回率(请参阅Nils Reimers的解释)。因此,在希望依赖关键字搜索的情况下,使用BM25 + 查询扩展来提高召回率是有意义的。
查询扩展
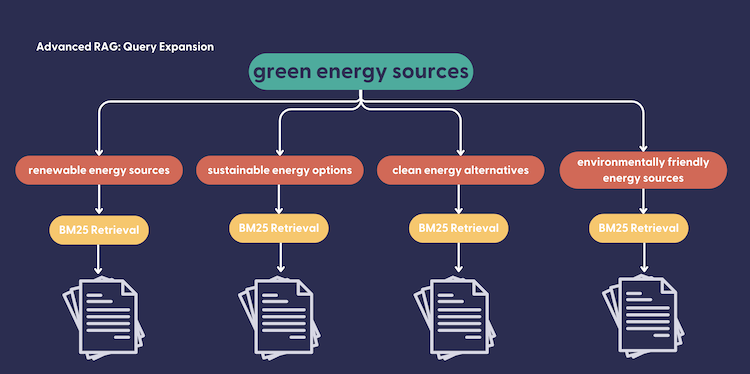
查询扩展是一种技术,我们将用户查询进行处理,并生成一定数量的相似查询。例如:
用户查询:“开源NLP框架”
查询扩展后:[“自然语言处理工具”,“免费NLP库”,“开源语言处理平台”,“带开源代码的NLP软件”,“开源NLP框架”]
这有助于改进检索结果,从而提高RAG结果的质量,尤其是在以下情况:
- 用户查询含糊不清或格式不正确。
- 在基于关键字的检索情况下,它还可以通过具有相似含义或同义词的查询来涵盖所有可能性。
以“全球变暖”为例,查询扩展将使我们能够确保我们也搜索“气候变化”或类似查询。
让我们首先导入实验性的QueryExpander组件。该组件使用OpenAI模型(在此案例中为gpt-4o-mini)来生成一定数量的与原始用户查询相似的附加查询。它返回查询,其中包含原始查询以及生成的相似查询。
expander = QueryExpander()
expander.run(query="open source nlp frameworks", number=4)
这将导致该组件返回包含原始查询+4个扩展查询的queries。
{'queries': ['natural language processing tools',
'free nlp libraries',
'open-source language processing platforms',
'NLP software with open-source code',
'open source nlp frameworks']}
带查询扩展的检索
让我们看看当我们将查询扩展作为一个检索管道的步骤时会发生什么。我们将通过一个非常简单的小型演示来了解这一点。为此,我使用了一些示例文档。这是我使用的documents列表:
documents = [
Document(content="The effects of climate are many including loss of biodiversity"),
Document(content="The impact of climate change is evident in the melting of the polar ice caps."),
Document(content="Consequences of global warming include the rise in sea levels."),
Document(content="One of the effects of environmental changes is the change in weather patterns."),
Document(content="There is a global call to reduce the amount of air travel people take."),
Document(content="Air travel is one of the core contributors to climate change."),
Document(content="Expect warm climates in Turkey during the summer period."),
]
当使用InMemoryBM25Retriever(即,我们进行关键字搜索)将查询“气候变化”的顶3个文档检索出来时,我们得到的排名前3位的候选文档是:
'Air travel is one of the core contributors to climate change.'
'The impact of climate change is evident in the melting of the polar ice caps.'
'The effects of climate are many including loss of biodiversity'
这里有2点需要注意:
- 我们只要求3个文档,并且我们得到了3个与查询“气候变化”相关的文档。从这个意义上说,这次检索完全有效,并且做得很好。
- 但是,由于我们将查询“气候变化”与关键字检索器结合使用,我们实际上可能会错过一些可能与查询更相关的文档。例如,“全球变暖”的文档完全被遗漏了。
您可以开始看到,在用户在搜索框中输入含糊不清的查询或关键字的情况下,这可能会如何影响您获得的结果。
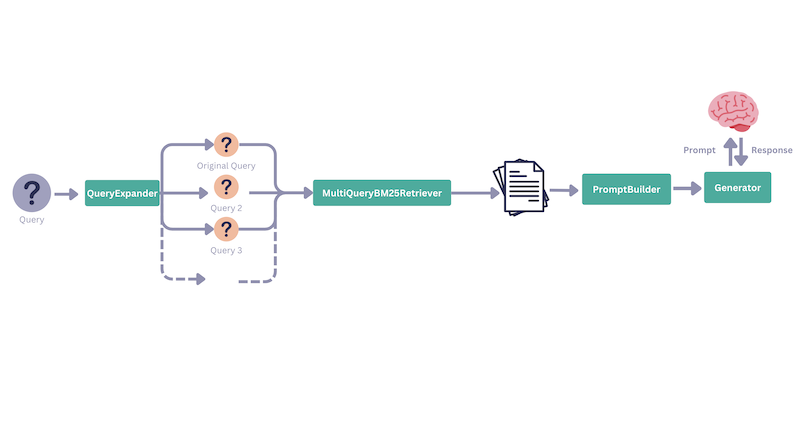
现在,让我们将查询扩展加入其中。这次我们将使用一个自定义检索器,称为MultiQueryInMemoryBM25Retriever,它可以接受一个queries列表而不是单个query(请参阅cookbook以获取完整代码)。这是我们创建的检索管道:
query_expander = QueryExpander()
retriever = MultiQueryInMemoryBM25Retriever(InMemoryBM25Retriever(document_store=doc_store))
expanded_retrieval_pipeline = Pipeline()
expanded_retrieval_pipeline.add_component("expander", query_expander)
expanded_retrieval_pipeline.add_component("keyword_retriever", retriever)
expanded_retrieval_pipeline.connect("expander.queries", "keyword_retriever.queries")
现在,我们可以再次使用相同的查询“气候变化”来运行此管道:
expanded_retrieval_pipeline.run({"expander": {"query": "climate change"}},
include_outputs_from=["expander"])
我们得到以下结果。查询扩展器已创建以下queries:
'expander': {'queries': ['global warming consequences',
'environmental impact of climate change',
'effects of climate variability',
'implications of climate crisis',
'consequences of greenhouse gas emissions',
'climate change']}}
请注意,您可能会获得不同的结果,因为您的
QueryExpander可能会生成不同的queries。
我们从检索管道收到了以下文档:
'Consequences of global warming include the rise in sea levels.'
'The impact of climate change is evident in the melting of the polar ice caps.',
'There is a global call to reduce the amount of air travel people take.'
'The effects of climate are many including loss of biodiversity'
'One of the effects of environmental changes is the change in weather patterns.'
'Air travel is one of the core contributors to climate change.'
请注意,我们能够添加关于“全球变暖”和“环境变化的影响”的上下文。
将查询扩展用于RAG
在示例 Cookbook 中,我们还添加了一个关于对维基百科页面使用查询扩展进行RAG的部分。我们将以下维基百科页面索引到InMemoryDocumentStore中:
"Electric_vehicle", "Dam", "Electric_battery", "Tree", "Solar_panel", "Nuclear_power",
"Wind_power", "Hydroelectricity", "Coal", "Natural_gas",
"Greenhouse_gas", "Renewable_energy", "Fossil_fuel"
然后,我们构建一个RAG管道。对于我们发送给LLM的最终提示,我们还指明了用户的原始查询是什么。
template = """
You are part of an information system that summarises related documents.
You answer a query using the textual content from the documents retrieved for the
following query.
You build the summary answer based only on quoting information from the documents.
You should reference the documents you used to support your answer.
###
Original Query: "{{query}}"
Retrieved Documents: {{documents}}
Summary Answer:
"""
query_expander = QueryExpander()
retriever = MultiQueryInMemoryBM25Retriever(InMemoryBM25Retriever(document_store=doc_store))
prompt_builder = PromptBuilder(template = template)
llm = OpenAIGenerator()
query_expanded_rag_pipeline = Pipeline()
query_expanded_rag_pipeline.add_component("expander", query_expander)
query_expanded_rag_pipeline.add_component("keyword_retriever", retriever)
query_expanded_rag_pipeline.add_component("prompt", prompt_builder)
query_expanded_rag_pipeline.add_component("llm", llm)
query_expanded_rag_pipeline.connect("expander.queries", "keyword_retriever.queries")
query_expanded_rag_pipeline.connect("keyword_retriever.documents", "prompt.documents")
query_expanded_rag_pipeline.connect("prompt", "llm")
使用查询扩展器运行此管道,使用简单的查询“绿色能源来源”,我们能够获得一个由维基百科页面构建的响应,包括“电动汽车”、“风力发电”、“可再生能源”、“化石燃料”和“核能”。没有MultiQueryInMemoryBM25Retriever,我们将依赖于对查询“绿色能源来源”进行单次BM25检索的顶k结果,从而得到一个由“可再生能源”、“风力发电”和“化石燃料”页面构建的响应。
总结
查询扩展是一项出色的技术,它允许您在仍使用关键字搜索的同时,获得更广泛的相关资源。虽然语义搜索是一个很好的选择,但它需要使用嵌入模型,并且需要对我们将进行搜索的数据源进行嵌入。这使得基于关键字的搜索成为更快、更便宜检索的非常有吸引力的选择。
然而,这确实意味着我们高度依赖于所提供查询的质量。查询扩展允许您通过生成与用户查询相似的查询来解决此问题。
在我看来,这项技术的主要优势之一是,它允许您避免在每次更新时对文档进行嵌入,同时在查询时仍能提高检索文档的相关性。关键字检索不需要任何额外的嵌入步骤,因此在此场景下检索时唯一发生的推理是当我们要求LLM生成一定数量的相似查询时。

