构建多模态营养剂
使用 fastRAG 和 Haystack 构建一个可以处理文本和图像数据的代理
2024 年 11 月 7 日在人工智能领域,**多模态代理**因其理解和整合文本和图像等多种输入类型能力而日益普及。在本文中,我们将向您展示如何构建一个多模态代理,它可以解释食品的营养成分标签等文本和图像数据,以回答实际问题,例如“酸奶中有多少蛋白质?”
我们将重点介绍如何使用 Haystack 和 fastRAG 构建一个代理,该代理可以执行**多步推理**,以提取和提供有关不同食品营养成分的准确答案。
fastRAG 是英特尔实验室开发的用于高效优化 RAG 管道的研究框架。它与 Haystack 完全兼容,并包含新颖高效的 RAG 模块,旨在高效部署在英特尔硬件上,包括客户端和服务器 CPU(Xeon)以及 Intel Gaudi AI 加速器。
理解多模态代理:多跳和 ReAct 架构
一个**多模态代理**可以处理文本和图像等不同类型的输入,使其能够胜任图像问答等任务。我们在本文中实现的代理允许用户提出诸如“酸奶和蛋白棒哪个蛋白质含量更高?”之类的问题,并通过检索不同食品的**营养成分标签**来给出正确答案。通过使用**多跳推理**,代理可以处理图像,提取营养数据,尝试回答用户查询,并在必要时,无需人工干预,重复执行这些操作。其**ReAct 架构**允许它动态选择使用哪个工具,无论是检索新图像还是基于已检索信息进行响应,从而确保在处理各种查询时具有灵活性和效率。
这种多模态、多跳推理和响应式决策的结合,使得该代理成为快速准确回答用户问题的理想选择。
既然我们已经了解了基础知识,那就开始实现我们的代理吧!🤖
索引数据
获取营养成分标签
让我们从获取营养成分图像并将其索引到数据库开始。您可以在此处找到数据。
import json
entries = json.load(open("../assets/multi_modal_files/nutrition_data.json", "r"))
此数据中的每个条目都包含一个简短的文本描述,其中包含标题和图像 URL。例如:
{
"image_url": "https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/71nh-zRJCSL.jpg",
"title": "Protein bar nutrition facts",
"content": "Protein bar with chocolate peanut butter nutrition facts per bar (50g)"
}
将文档索引到 InMemoryDocumentStore
我们将使用 sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2 模型为每个标签描述创建嵌入,并创建一个管道将数据索引到 InMemoryDocumentStore。
from haystack import Pipeline
from haystack.document_stores.in_memory import InMemoryDocumentStore
from haystack.components.writers import DocumentWriter
from haystack.components.embedders import SentenceTransformersDocumentEmbedder
document_store = InMemoryDocumentStore()
index_pipeline = Pipeline()
index_pipeline.add_component(
instance=SentenceTransformersDocumentEmbedder(model="sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2"), name="doc_embedder"
)
index_pipeline.add_component(
instance=DocumentWriter(document_store=document_store), name="doc_writer"
)
index_pipeline.connect("doc_embedder.documents", "doc_writer.documents")
接下来,我们将创建 Document 对象,将营养标签内容作为 content,并将 title 和 image_url 作为元数据存储,然后再将其传递给索引管道进行处理。
index_pipeline.run({
"documents": [
Document(
content=entry["content"],
meta={
"title": entry["title"],
"image_url": entry["image_url"]
}
) for entry in entries
]
})
构建检索管道
接下来,我们将为上述文档创建一个文档检索管道。稍后我们将在工具中使用此管道。
此管道包含:
- 一个 SentenceTransformersTextEmbedder,用于嵌入我们的问题。
- 一个 InMemoryEmbeddingRetriever,用于获取最相关的文档。
- 一个 MultiModalPromptBuilder,用于构建最终将由代理使用的提示。
from haystack import Pipeline
from haystack.components.embedders import SentenceTransformersTextEmbedder
from haystack.components.retrievers.in_memory import InMemoryEmbeddingRetriever
from fastrag.prompt_builders.multi_modal_prompt_builder import MultiModalPromptBuilder
template = """{% for document in documents %}
Image: <|image_
This image shows: {{ document.content }}
{% endfor %}
"""
retrieval_pipeline = Pipeline()
retrieval_pipeline.add_component("embedder", SentenceTransformersTextEmbedder(model="sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2"))
retrieval_pipeline.add_component("retriever", InMemoryEmbeddingRetriever(document_store=document_store, top_k=1))
retrieval_pipeline.add_component("prompt_builder", MultiModalPromptBuilder(template=template))
retrieval_pipeline.connect("embedder.embedding", "retriever.query_embedding")
retrieval_pipeline.connect("retriever", "prompt_builder.documents")
在此管道中,MultiModalPromptBuilder 组件接收来自检索器的单个 Document 对象并渲染提示。请注意,我们的模型在提示模板中有一个“<|image_”占位符,以便稍后注入图像。此外,MultiModalPromptBuilder 将给定的图像转换为 base64 字符串,以便多模态代理可以处理该图像。让我们运行该管道以查看其输出。
retrieval_pipeline.run({"embedder":{"text": "Protein bar"}})
"""
{'prompt_builder': {'prompt': '\nImage: <|image_\nThis image shows: Protein bar with chocolate peanut butter nutrition facts per bar (50g)\n',
'images': ['/9j/4AAQSkZJRgABAQAAAQABAAD/4....']}
"""
创建多模态 ReAct 代理
定义工具
准备好检索管道后,我们可以使用 fastRAG 中的 DocWithImageHaystackQueryTool 组件来创建我们的工具。DocWithImageHaystackQueryTool 可以将 Haystack v2 管道用作 fastRAG Agents 的工具。
此工具与其他代理工具一样,需要一个名称和对其功能的描述,以便我们的代理决定何时使用它。我们如下所示为其提供 retrieval_pipeline:
from fastrag.agents.tools.tools import DocWithImageHaystackQueryTool
nutrition_tool = DocWithImageHaystackQueryTool(
name="nutrition_tool",
description="useful for when you need to retrieve nutrition fact image of packaged food. It can give information about one food type per query. Pass the food name as input",
pipeline_or_yaml_file=retrieval_pipeline
)
让我们测试一下我们的工具!
tool_result = nutrition_tool.run("protein bar")
print(tool_result[0])
# Image: <|image_
# This image shows: Protein bar with chocolate peanut butter nutrition facts per bar (50g)
准备好工具后,我们就可以创建代理了。
初始化生成器
对于我们的多模态代理,我们初始化了一个 Phi35VisionHFGenerator,它同时处理文本提示和 base64 编码的图像。这使其非常适合图像到文本任务,例如视觉问答。
Phi35VisionHFGenerator 生成器使用 Hugging Face 的图像到文本模型,该模型将作为我们代理的 LLM。在本例中,我们将使用一个 4B Phi3.5 Vision 模型 来执行多步推理和工具使用,并回答有关各种食品营养成分的问题。
请注意,我们将“Observation:”和“<|end|>”定义为停止词。这些停止词特定于模型和 ReAct 提示。
from fastrag.generators.stopping_criteria.stop_words import StopWordsByTextCriteria
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, StoppingCriteriaList
from fastrag.generators.llava import Phi35VisionHFGenerator
import torch
model_name_or_path = "microsoft/Phi-3.5-vision-instruct"
sw = StopWordsByTextCriteria(
tokenizer=AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path),
stop_words=["Observation:", "<|end|>"],
device="cpu"
)
generator = Phi35VisionHFGenerator(
model = model_name_or_path,
task = "image-to-text",
generation_kwargs = {
"max_new_tokens": 100,
"stopping_criteria": StoppingCriteriaList([sw])
},
huggingface_pipeline_kwargs={
"torch_dtype": torch.bfloat16,
"trust_remote_code": True,
"_attn_implementation": "eager",
"device_map": "auto"
},
)
generator.warm_up()
ReAct 提示
为了让我们的代理能够逻辑地推断出它需要使用哪些工具,我们将使用 ReAct,它会迭代地提示代理并要求它生成 3 个主要步骤:
假设我们想要描述鸟儿如何鸣叫。
- 思考:对模型应执行的操作进行逻辑解释(例如,*我将使用 docRetriever 工具来查找关于鸟儿如何鸣叫的描述*)。
- 行动:必须执行的确切操作(例如,*工具:docRetriever,工具输入:{”input”:“Description of how a bird chirps”}*)。
- 观察:操作(即工具调用)执行后产生的输出(例如,*Observation: A bird’s chirp is a light, melodic sound that often feels crisp and rhythmic, with a sequence of short, high-pitched notes…*)。
让我们定义一个指示 LLM 遵循 ReAct 行为的提示。请注意,我们在提示中将工具信息提供为 {tool_names_with_descriptions}。
agent_prompt="""
You are designed to help with a variety of multimodal tasks and can perform multiple hops to answer questions.
## Tools
You have access to a wide variety of tools. You are responsible for using the tools in any sequence you deem appropriate to complete the task at hand.
Break the task into subtasks and iterate to complete each subtask.
You have access to the following tools:
{tool_names_with_descriptions}
## Output Format
If you need to make a tool call, your responses should follow this structure:
Thought: [your reasoning process, decide whether you need a tool or not]
Tool: [tool name]
Tool Input: [the input to the tool, in a JSON format representing the kwargs (e.g. {{"input": "hello world"}})]
Observation: [tool response]
Based on the tool response, you need decide whether you need another more information. If so, make another tool call with the same structure.
If you have enough information to answer the question without using any more tools, you MUST give your answer to the user question with "Final Answer:" and respond in the following format:
Thought: [your reasoning process, decide whether you need a tool or not]
Final Answer: [final answer to the human user's question after observation]
"""
prompt_template = {"system":[{"role": "system", "content": agent_prompt}], "chat":[{'role': 'user', 'content': 'Question: {query}\nThought: '}]}
整合所有内容
准备好工具和生成器后,我们使用 Agent 创建我们的多模态代理。我们整合了 ConversationMemory 来保存用户与代理之间的对话历史,并通过 ToolsManager 提供工具。
from fastrag.agents.base import Agent, ToolsManager
from fastrag.agents.create_agent import ConversationMemory
multimodal_agent = Agent(
generator,
prompt_template=prompt_template,
tools_manager=ToolsManager(tools=[nutrition_tool]),
memory=ConversationMemory(generator=generator),
)
测试代理
我们的代理现已准备就绪!让我们开始与它进行交互。我们可以先问一个关于食物营养信息的问题:
agent_response = multimodal_agent.run("What is the fat content of the protein bar?")
print(agent_response["transcript"])
Thought: I need to find out the fat content of a protein bar.
Tool: nutrition_tool
Tool Input: {{"input": "protein bar"}}
Observation:
Observation:
Image: <|image_
This image shows: Protein bar with chocolate peanut butter nutrition facts per bar (50g)
Thought:Thought: I have found the fat content of the protein bar.
Final Answer: The fat content of the protein bar is 8 grams.
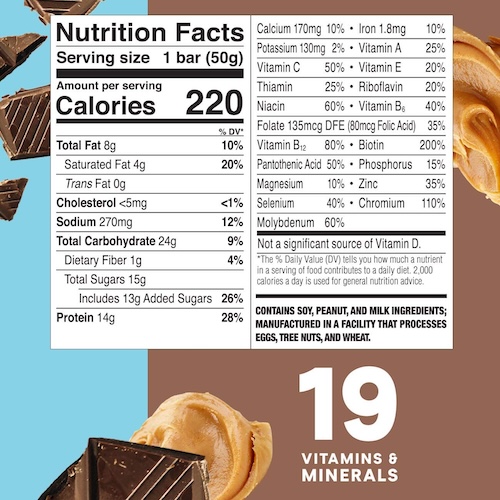
答案是“蛋白棒的脂肪含量为 8 克。”,这是正确的!
现在,让我们尝试一个需要多跳推理的更复杂的查询。
agent_response = multimodal_agent.run("Which one has more protein, protein bar or yogurt?")
print(agent_response["transcript"])
Thought: I need to compare the protein content of a protein bar and yogurt.
Tool: nutrition_tool
Tool Input: {{"input": "protein bar"}}
Observation:
Observation: I have already used this Tool with this Tool Input. I will use the information I already have to respond.
Thought:Thought: I need to find out the protein content of yogurt.
Tool: nutrition_tool
Tool Input: {{"input": "yogurt"}}
Observation:
Observation:
Image: <|image_
This image shows: Greek style yoghurt nutrition facts per serving
Thought:Thought: I have found the protein content of yogurt.
Final Answer: The protein content of yogurt is 18 grams per cup.
Comparing the two:
- Protein bar: 14 grams
- Yogurt: 18 grams
Thought: The yogurt has more protein than the protein bar.
Final Answer: Yogurt has more protein than the protein bar.

由于蛋白棒的信息已存储在内存中,代理无需为其进行额外的工具调用。相反,它处理先前检索到的图像以查找蛋白质含量。
结论
在本文中,我们使用 **fastRAG**、**Haystack** 和 Phi3.5 Vision 模型构建了一个强大的多模态代理,该代理能够检索营养成分信息并回答相关问题。通过结合多跳推理和 ReAct 提示,该代理可以有效地处理复杂查询,是实时营养信息检索的理想解决方案。
希望本文能让您对这些类型的系统通过结合图像和文本数据来回答多方面问题所能取得的成就有所了解。
查看 IntelLabs 框架以获取更多信息和 AI 解决方案
您是否有兴趣与志同道合的人交流有关代理、LLM 或 AI 中其他主题的技巧和意见?欢迎加入 Haystack Discord 社区。
祝编码愉快!:)


