善于倾听:记忆如何赋能对话式代理
……以及我们在 Haystack 中是如何实现的
2023年7月7日记忆是将强大的 LLM 转变为能够记住你之前说过什么的富有同情心的对话者的关键。但它是如何工作的呢?
今天,我们想揭秘 Haystack 中记忆的实现方式。我们将解释记忆注入和记忆作为工具的区别,并向您展示如何通过总结来克服上下文窗口长度的限制。
如果您想了解记忆在计算上是如何工作的,或者开始使用 Haystack 构建自己的对话式 AI 界面,那么本文适合您。
为什么记忆很重要
要让言语交流感觉像一次对话,双方都需要某种形式的记忆:他们需要记住之前说过的话,并且能够通过使用代词等方式来指代重要的实体和概念。
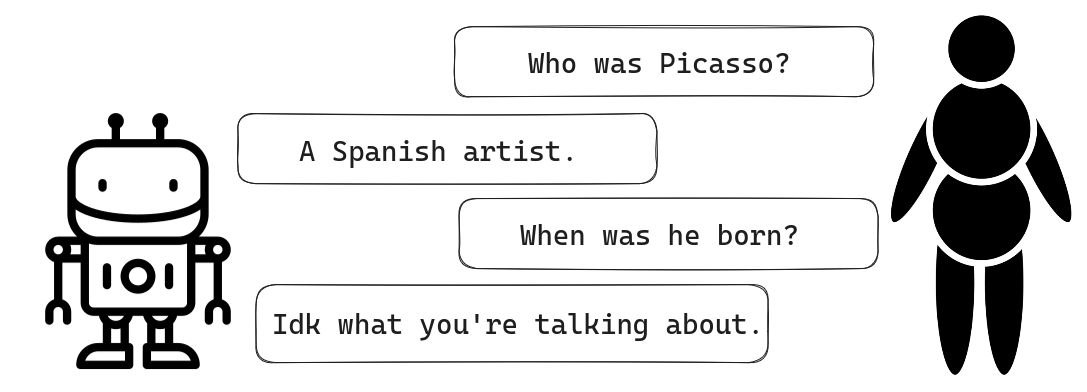
考虑以下来自电影《Booksmart》的对话:
Amy:说出一个因为打破了几条规则而生活因此变得更好的人。
Molly:毕加索。
Amy:他打破的是艺术规则。说出一个打破了真正规则的人。
Molly:罗莎·帕克斯。
Amy:再说一个。
Molly:苏珊·B·安东尼。
Amy:该死。
这次对话之所以能够进行,仅仅是因为 Amy 和 Molly 知道之前说过什么。从上下文中可以清楚地看出,代词“他”指的是毕加索,当 Amy 说“再说一个”时,她不必拼写出她指的是“另一个打破规则的人”。
大型语言模型与记忆
默认情况下,LLM 没有内置的记忆概念。就开箱即用的 LLM 而言,它收到的每个提示都标志着一次全新的互动。
为了让对话感觉自然,一个高级的聊天机器人需要具备超越当前问答对的上下文。这种特性被称为记忆或历史。

为了让对话式代理了解先前的交流,存在不同的记忆实现方式。
代理的记忆注入
Haystack 中的对话式代理是一个基本的聊天机器人,可以通过 LLM 生成用户查询的答案。记忆会与每个新查询一起传递到提示中。

正如图所示,记忆存储了代理的每个答案以及用户的查询。在此实现中,记忆本质上是一个列表。人类和 AI 之间的每一次新交流都会附加到列表中,以便可以将其重新注入到下一个提示中。
为了说明这一点,让我们看一个包含多个交流的对话。我为这些示例使用了 OpenAI 的 gpt-3.5-turbo,也就是驱动 ChatGPT 的模型。(有关如何使用 Haystack 设置对话式代理的完整教程,请参阅我们的教程。)
首先,我们导入 PromptNode,并使用模型名称、OpenAI 的 API 密钥以及节点输出的最大长度对其进行初始化。
from haystack.nodes import PromptNode
model_name = 'gpt-3.5-turbo'
prompt_node = PromptNode(model_name, api_key=MY_API_KEY, max_length=256)
现在,我们可以通过将提示节点传递给它来设置我们的对话式代理(又名聊天机器人)。默认情况下,这会初始化一个记忆,该记忆会在每次新调用时被注入到用户的提示中。
from haystack.agents.conversational import ConversationalAgent
conversational_agent = ConversationalAgent(prompt_node=prompt_node)
现在让我们向模型提出几个问题来累积一些记忆。
conversational_agent.run("Who was Pablo Picasso?")
>>> Pablo Picasso was a renowned Spanish artist who is considered one of the most influential artists of the 20th century. He is known for co-founding the Cubist movement and for his contributions to Surrealism. His work encompasses various styles and mediums, including painting, sculpture, ceramics, and collage.
通过在下一个查询中引用画家并使用代词,我们可以轻松验证记忆注入是否有效。
conversational_agent.run("Where did he live?")
>>> Picasso was born in Malaga, Spain, but he spent most of his adult life in France, particularly in Paris. He also had periods of residency in Barcelona and various other locations throughout Europe.
有意思!但现在到最关键的问题了。
conversational_agent.run("How can I learn to paint like him?")
>>> To learn to paint like Picasso, you can start by studying his works and understanding his artistic style. Analyze his use of color, form, and composition. Experiment with different techniques and mediums that he used, such as Cubism or collage. Practice regularly and don't be afraid to take risks with your art.
我们现在可以通过调用来更仔细地查看代理的记忆。
print(conversational_agent.memory.load())
>>> Human: Who was Pablo Picasso?
AI: Pablo Picasso was a renowned Spanish artist who is considered one of the most influential artists of the 20th century. He is known for co-founding the Cubist movement and for his contributions to Surrealism. His work encompasses various styles and mediums, including painting, sculpture, ceramics, and collage.
Human: Where did he live?
AI: Picasso was born in Malaga, Spain, but he spent most of his adult life in France, particularly in Paris. He also had periods of residency in Barcelona and various other locations throughout Europe.
Human: How can I learn to paint like him?
AI: To learn to paint like Picasso, you can start by studying his works and understanding his artistic style. Analyze his use of color, form, and composition. Experiment with different techniques and mediums that he used, such as Cubism or collage. Practice regularly and don't be afraid to take risks with your art.
显然,我们与模型的所有交流都已存储在记忆中。这也清楚地说明了为什么使用此解决方案,您可能会很快遇到问题。随着人类和 AI 之间对话的进行,以及记忆中先前交流列表的增长,LLM 的上下文窗口可能会变得太小。当提示开始溢出上下文窗口时,模型的输出质量会下降。
成本是另一个因素:像 OpenAI 这样的公司会根据 token 收费,因此您希望保持提示简短。作为一种解决方案,您可以定期总结您的记忆。
总结记忆
通过使用一个单独的模型定期总结您的代理的记忆,您可以使记忆保持可管理。在 Haystack 中,您可以初始化一个对话摘要记忆,该记忆可以生成对最近几次人类和 AI 之间交流的摘要。在我们的示例中,我们将使用与对话式代理相同的模型进行总结——因此我们再次使用提示节点初始化记忆。
from haystack.agents.memory import ConversationSummaryMemory
summary_memory = ConversationSummaryMemory(prompt_node)
请注意,此记忆类使用特定的提示模板,该模板指示模型压缩对话。稍后我们将看到如何自己调整这些说明。让我们再次初始化对话式代理,这次使用我们的摘要记忆。
from haystack.agents.conversational import ConversationalAgent
conversational_agent = ConversationalAgent(prompt_node=prompt_node, memory=summary_memory)
在用与之前相同的 <$>提问< $>运行此代理后,我们再次查看记忆。
print(conversational_agent.memory.load())
>>> Pablo Picasso was a highly influential Spanish artist known for his contributions to various art movements. He lived in Spain and France.
Human: How can I learn to paint like him?
AI: To learn to paint like Picasso, you can start by studying his works and understanding his artistic style. Analyze his use of color, form, and composition. Experiment with different techniques and mediums that he used, such as Cubism or collage. Practice regularly and don't be afraid to take risks with your art.
我们可以看到,通过使用摘要,我们已经大大压缩了我们的记忆。有趣的是,模型决定几乎完整地保留最后一次交流。
默认情况下,节点在三次交流后创建一个摘要,但您可以通过调整 summary_frequency 参数来更改它。您甚至可以将该参数设置为 1,在每次交流后创建一个摘要。在下一个示例中,我们将执行此操作,并指示模型使记忆 extra short(最多十个单词)。为此,我们导入提示模板类,并在自定义模板中指定我们的要求,然后将其传递给摘要记忆。
from haystack.agents.memory import ConversationSummaryMemory
from haystack.nodes import PromptTemplate
my_template = PromptTemplate("Create a short summary (max 10 words) of the following chat transcript by shortening and summarizing the content without losing important information:\n{chat_transcript}\nCondensed Transcript:",)
summary_memory = ConversationSummaryMemory(prompt_node, prompt_template=my_template, summary_frequency=1)
使用新的提示模板后,三次交流后我们的记忆是什么样的?
print(conversational_agent.memory.load())
>>> Picasso: Influential Spanish painter known for Cubism and innovation.Picasso lived in Spain, France, and the United States.Study Picasso's style, experiment with materials, take art classes.
我们已经大大缩短了我们的记忆,同时保留了所有重要信息!
该示例使用了 OpenAI 的专有模型。尽管如此,您也可以将我们的对话摘要记忆类与 Hugging Face 模型中心的开源模型一起使用。一个不错的选择是这个 BART-large 模型,它专为总结对话而设计。但请注意,旧模型无法像 LLM 那样遵循指令。为了使其工作,您可以使用以下代码:
summary_node = PromptNode('philschmid/bart-large-cnn-samsum', max_length=256, model_kwargs={"task_name": "text2text-generation"})
template = PromptTemplate("{chat_transcript}")
summary_memory = ConversationSummaryMemory(summary_node, prompt_template=template)
请注意,虽然上述解决方案设法使记忆比我们最初使用的累加版本短得多,但由于摘要被附加,它们仍然导致记忆不断增长。此开放问题旨在解决此问题,方法是总结整个记忆,从而允许您在整个对话中将其保持在稳定长度。
带工具的对话式代理的记忆
对话式代理允许您设置基本的聊天机器人功能。但这远远没有发挥代理提供的所有功能。代理之所以如此强大,是因为它们可以利用 LLM 的推理能力进行动态解决方案规划:给定一组工具,代理可以自行决定使用这些工具以得出最佳最终答案。
代理会跟踪它们的思考过程—— dẫn đến câu trả lời cuối cùng của chúng - trong một “bản ghi”. Nếu bạn không muốn chuyển cả bản ghi bộ nhớ và bản ghi cho tác nhân hội thoại, bạn có thể đơn giản triển khai bộ nhớ dưới dạng một công cụ khác.
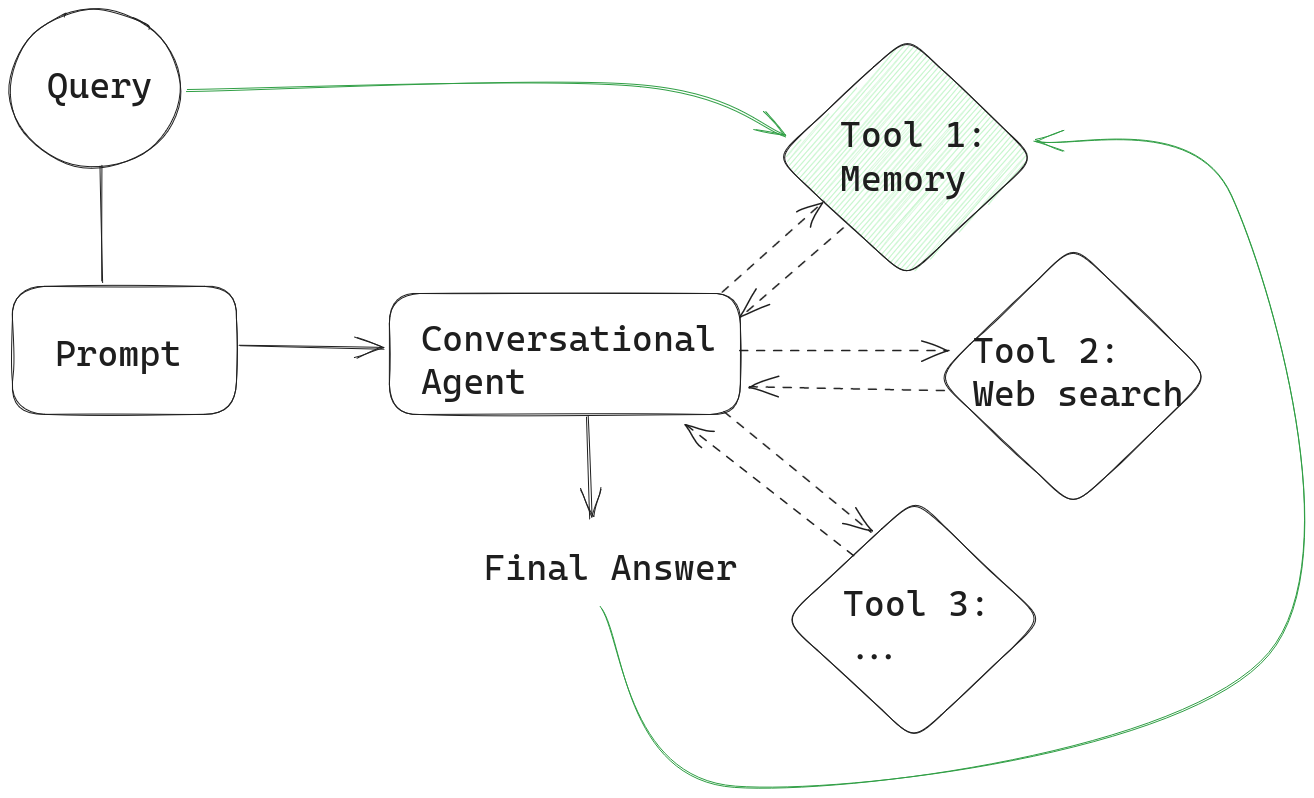
在此设置中,代理在收到提示后,首先会咨询记忆工具,看看它是否能为回答用户查询提供任何上下文。然后,在每次迭代后,代理的输出会与查询一起存储在记忆中,就像我们之前的示例一样。
记忆作为工具为我们打开了一系列可能性。您可以自由地将其配置为您认为最有效的方式。也许您想在记忆数据库中跟踪大量人类-AI 交互。然后,您可以通过诸如抽取式 QA 管道或摘要管道等复杂工具来服务您的记忆。
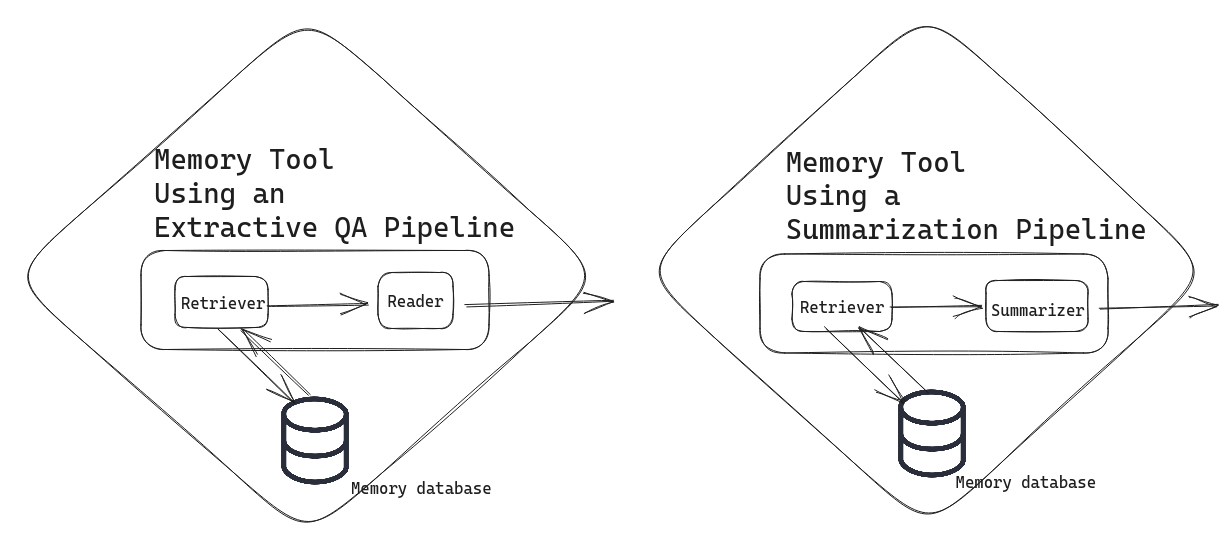
在抽取式 QA 管道解决方案中,您的对话式代理会将查询发送到您的记忆数据库,然后该管道会尝试从有助于语境化用户查询的记忆中返回最相关的片段。在摘要管道解决方案中,记忆工具会返回相关文档的摘要。将记忆实现为这些工具可以再次帮助您避免遇到 LLM 的 token 限制。
别忘了关注我们
作为一家公司,deepset 致力于将 LLM 应用于每个应用程序。我们也喜欢与我们的社区分享所有 NLP 的最新见解。如果您觉得不错,请在 Twitter 上关注我们。
我们的 OSS 框架 Haystack 提供了构建最先进 LLM 系统所需的所有工具。前往 Haystack GitHub 仓库了解更多信息。
要了解其他人正在使用 Haystack 构建什么,或者如果您需要帮助来处理您自己的项目,请加入我们的 Discord 服务器。这是一个由我们的 Devrel 倡导者管理的友好社区,您可以在那里遇到其他对 NLP 感兴趣的人。

