用 Haystack 与 SQL 数据库聊天
使用 Haystack 用自然语言与 SQL 对话
2024年4月22日让我们谈谈如何构建能够与 SQL 数据库交互甚至聊天的 AI 应用程序。请注意,这是一个我尝试过的小项目,它是用自然语言与 SQL 交互的非常简单的方法。我 *确定* 它并非能处理所有类型 SQL 表等的万能方法。但,尽管如此,它很酷,能正常工作,你可以和我一起尝试。
我开始这个项目的目标是能够用自然语言提问,并根据 SQL 数据库的内容获得答案。例如,假设我们有一个数据库,存储着关于员工及其工作时间的信息;“*有多少人每天工作超过 8 小时?*”,“*总共有 20 名员工每天工作超过 8 小时。*”。
我预料到一个基于生成式 LLM 的系统可能会遇到的一些困难
- 如果问题与 SQL 数据库的内容 *不相关* 怎么办?
- 我可以让 LLM 生成一个 SQL 查询,但我该如何实际查询数据库?
- 如果 SQL 查询 *错了* 怎么办?🙂
所以,这里是我做的 4 件事,并且我在这里向你展示。并非所有都解决了上述所有问题,但它们是一个很好的起点。另外请注意,我在此项目中使用的是 Haystack,因此接下来的演示将包含一些 Haystack 的术语。
- 我创建了一个 *可以查询 SQL 数据库* 的组件。我使用了 SQLite。
- 我创建了一个 *使用 LLM 的管道,该 LLM 可以接收问题,根据我数据库的结构生成 SQL 查询,并执行查询*
- 接下来,为了解决“如果查询不相关怎么办”的问题,我将我的管道“升级”为使用 *条件路由*。
- 最后,为了获得真正的聊天体验,我改变了策略,将所有内容定义为函数,并使用了最新 LLM 的 *函数调用* 功能。然后我将其包装成一个微型的 Gradio 应用,你可以从我提供的食谱中运行它。
在我们深入研究之前,关于手头的数据有一个快速说明。我不会在这里展示将数据放入数据库的所有代码,因为说实话,那是最无聊的一步……几点说明
- 我使用了一个名为“Absenteeism_at_work”的 CSV 文件,JupySQL 团队使用它来展示他们的示例。非常方便!我从*我们之前与他们创建的第一个演示*中汲取灵感,并将这个表写入了我的 SQLite 数据库。
- 生成的表具有以下列
ID;Reason_for_absence;Month_of_absence;Day_of_the_week;Seasons;Transportation_expense;Distance_from_Residence_to_Work;Service_time;Age;Work_load_Average_day_;Hit_target;Disciplinary_failure;Education;Son;Social_drinker;Social_smoker;Pet;Weight;Height;Body_mass_index;Absenteeism_time_in_hours
- 我已填充一个名为
absenteeism.db的数据库,它代表了这个表,我们将在此之后一直使用它。
🧑🍳 你可以在*提供的食谱*中查看和运行所需的所有 SQL 数据库设置代码。
第一部分:用自然语言查询 SQL
首先,让我们处理最简单的部分。让我们创建一个管道,它将
- 接收一个问题
- 创建一个 SQL 查询
- 实际查询我们的数据库。
为此,我们需要这个。一个 SQLQuery 组件,Haystack 没有提供。但 Haystack *确实* 提供了一个创建组件的统一接口。这是我的样子
import sqlite3
from typing import List
from haystack import component
@component
class SQLQuery:
def __init__(self, sql_database: str):
self.connection = sqlite3.connect(sql_database, check_same_thread=False)
@component.output_types(results=List[str], queries=List[str])
def run(self, queries: List[str]):
results = []
for query in queries:
result = pd.read_sql(query, self.connection)
results.append(f"{result}")
return {"results": results, "queries": queries}
现在我有了 SQLQuery 组件,我可以用 sql_query = SQLQuery('absenteeism.db) 来初始化它。
为了测试它,我可以用这个组件运行以下 SQL 查询
result = sql_query.run(queries=['SELECT Age, SUM(Absenteeism_time_in_hours) as Total_Absenteeism_Hours FROM absenteeism WHERE Disciplinary_failure = 0 GROUP BY Age ORDER BY Total_Absenteeism_Hours DESC LIMIT 3;'])
print(result["results"][0])
结果是
Age Total_Absenteeism_Hours
0 28 651
1 33 538
2 38 482
构建 SQL 查询管道
现在我们有了一个能够接收 SQL 查询并查询我们所需数据库的组件,让我们将其作为步骤添加到完整的 AI 应用程序中。我们将构建一个 Haystack 管道,它将
- 使用一个提示,该提示指示 LLM(例如,我们这里使用 GPT-4,如果你想坚持使用它,你必须提供你的 API 密钥作为
OPENAI_API_KEY环境变量)根据我们数据库中存在的columns和我们提供的自然语言question来生成 SQL 查询。 - 将生成的 SQL 查询转发给我们新创建的
SQLQuery组件
from haystack import Pipeline
from haystack.components.builders import PromptBuilder
from haystack.components.generators.openai import OpenAIGenerator
prompt = PromptBuilder(template="""Please generate an SQL query. The query should answer the following Question: {{question}};
The query is to be answered for the table is called 'absenteeism' with the following
Columns: {{columns}};
Answer:""")
sql_query = SQLQuery('absenteeism.db')
llm = OpenAIGenerator(model="gpt-4")
sql_pipeline = Pipeline()
sql_pipeline.add_component("prompt", prompt)
sql_pipeline.add_component("llm", llm)
sql_pipeline.add_component("sql_querier", sql_query)
sql_pipeline.connect("prompt", "llm")
sql_pipeline.connect("llm.replies", "sql_querier.queries")
最终的 sql_pipeline 如下所示(在食谱中使用 sql_pipeline.show() 生成)👇
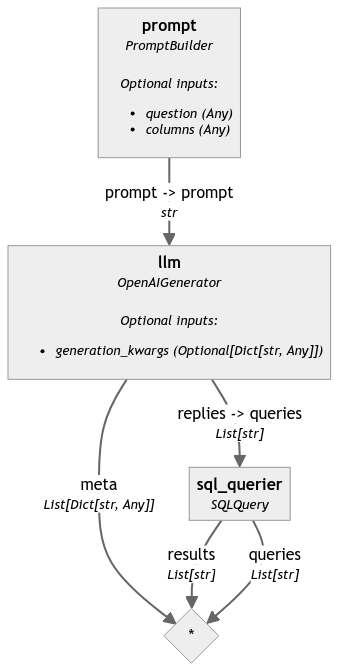
让我们尝试运行它,这是我们得到的结果 👇
result = sql_pipeline.run({"prompt": {"question": "On which days of the week does the average absenteeism time exceed 4 hours?",
"columns": columns}})
print(result["sql_querier"]["results"][0])
# Day_of_the_week
#0 2
#1 3
#2 4
#3 5
#4 6
第二部分:使用条件路由跳过不相关的问题
接下来,让我们做一个简单的改进。如果提供的 question 不相关怎么办?最好跳过它,而不是用会导致错误的 SQL 查询来查询数据库。
对于这一步,我使用了 [ConditionalRouter](https://docs.haystack.com.cn/docs/conditionalrouter)。
首先,让 LLM 在提供的问题无法用我们拥有的 SQL 表回答时回复 no_answer。
from haystack.components.builders import PromptBuilder
from haystack.components.generators.openai import OpenAIGenerator
prompt = PromptBuilder(template="""Please generate an SQL query. The query should answer the following Question: {{question}};
If the question cannot be answered given the provided table and columns, return 'no_answer'
The query is to be answered for the table is called 'absenteeism' with the following
Columns: {{columns}};
Answer:""")
llm = OpenAIGenerator(model="gpt-4")
接下来,让我们定义一些路由和我们的 ConditionalRouter。我们在这里想完成的是
- 如果 LLM 的回复是
no_answer,我们希望进入我们管道的go_to_fallback分支。 - 如果没有
no_answer,我们希望进入sql路由。
from haystack.components.routers import ConditionalRouter
routes = [
{
"condition": "{{'no_answer' not in replies[0]}}",
"output": "{{replies}}",
"output_name": "sql",
"output_type": List[str],
},
{
"condition": "{{'no_answer' in replies[0]}}",
"output": "{{question}}",
"output_name": "go_to_fallback",
"output_type": str,
},
]
router = ConditionalRouter(routes)
最后,让我们决定当我们要走备用路线时该怎么做。在这个例子中,我只是创建了一个 fallback_llm,它会告诉用户*为什么*无法回答这个问题。
fallback_prompt = PromptBuilder(template="""User entered a query that cannot be answerwed with the given table.
The query was: {{question}} and the table had columns: {{columns}}.
Let the user know why the question cannot be answered""")
fallback_llm = OpenAIGenerator(model="gpt-4")
当我们把所有这些以及我们的 sql_query 组件添加到一个管道中时,它看起来是这样的 👇
from haystack import Pipeline
conditional_sql_pipeline = Pipeline()
conditional_sql_pipeline.add_component("prompt", prompt)
conditional_sql_pipeline.add_component("llm", llm)
conditional_sql_pipeline.add_component("router", router)
conditional_sql_pipeline.add_component("fallback_prompt", fallback_prompt)
conditional_sql_pipeline.add_component("fallback_llm", fallback_llm)
conditional_sql_pipeline.add_component("sql_querier", sql_query)
conditional_sql_pipeline.connect("prompt", "llm")
conditional_sql_pipeline.connect("llm.replies", "router.replies")
conditional_sql_pipeline.connect("router.sql", "sql_querier.queries")
conditional_sql_pipeline.connect("router.go_to_fallback", "fallback_prompt.question")
conditional_sql_pipeline.connect("fallback_prompt", "fallback_llm")
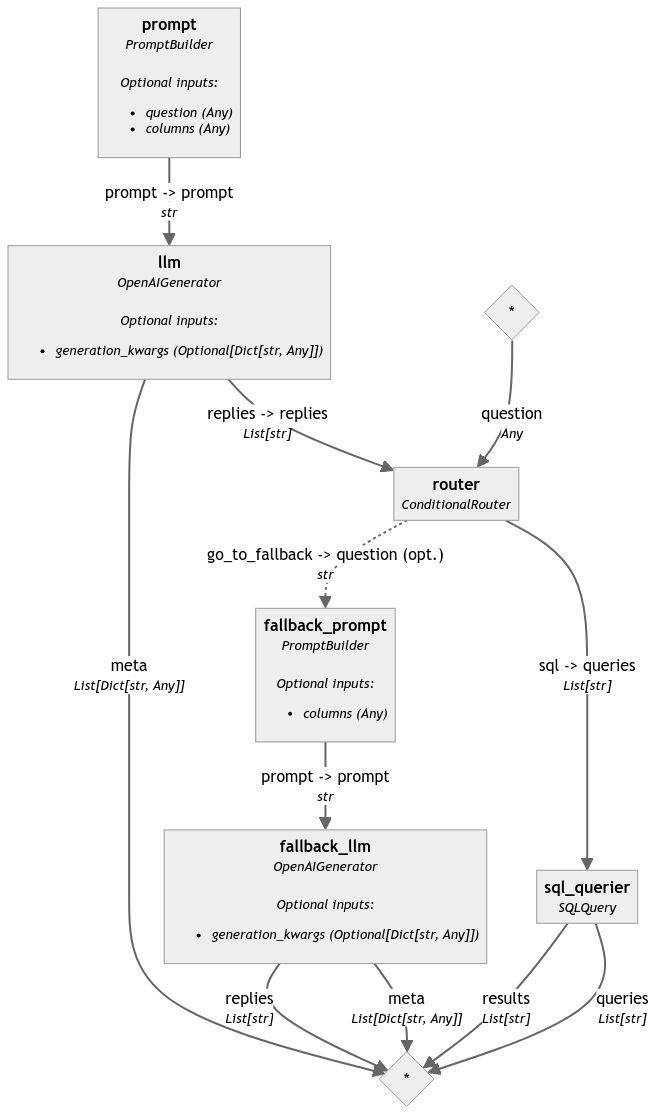
如果我问这个问题“一周中的哪几天平均缺勤时间超过 4 小时?”给这个管道,我得到
question = "On which days of the week does the average absenteeism time exceed 4 hours?"
result = conditional_sql_pipeline.run({"prompt": {"question": question,
"columns": columns},
"router": {"question": question},
"fallback_prompt": {"columns": columns}})
if 'sql_querier' in result:
print(result['sql_querier']['results'][0])
elif 'fallback_llm' in result:
print(result['fallback_llm']['replies'][0])
# Day_of_the_week
#0 2
#1 3
#2 4
#3 5
#4 6
但是如果我问“我的生日是什么时候?”我得到以下回复
由于提供的数据表中不包含生日等用户个人数据,因此无法回答该查询。该表主要关注与缺勤相关的数据,可能用于工作或类似情况。请提供相关数据以获得准确的答案。
第三部分:构建一个带函数调用的聊天应用(& Gradio)
我尝试的最后一件事是使用函数调用而不是条件路由。目的是与我们的 SQL 数据库进行类似人类的讨论。通过这样做,我们允许 LLM *决定* 是否应该选择该工具(我们的函数)来解决问题。生成的系统具有以下流程
- 用户提问
- LLM 决定提供的任何工具(函数)是否可以解决问题
- LLM 生成它选择使用的工具的输入。这些输入应该是工具实际运行所需的内容
- 我们使用生成的输入运行工具。
- 然后,LLM 根据工具返回的结果生成类似人类的答案。
我已经有了一个相当直接的 SQLQuery 组件,所以这是我如何将其包装成一个函数
sql_query = SQLQuery('absenteeism.db')
def sql_query_func(queries: List[str]):
try:
result = sql_query.run(queries)
return {"reply": result["results"][0]}
except Exception as e:
reply = f"""There was an error running the SQL Query = {queries}
The error is {e},
You should probably try again.
"""
return {"reply": reply}
由于我在这里使用 GPT-4 作为我的演示 LLM,我将把这个函数作为一个工具提供
tools = [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "sql_query_func",
"description": f"This a tool useful to query a SQL table called 'absenteeism' with the following Columns: {columns}",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"queries": {
"type": "array",
"description": "The query to use in the search. Infer this from the user's message. It should be a question or a statement",
"items": {
"type": "string",
}
}
},
"required": ["question"],
},
},
}
]
一旦就位,我只需将其作为工具添加到 OpenAIChatGenerator 中,然后创建一个跟踪对话历史的微型应用程序。我使用了 Gradio(感谢 Bilge 在*构建带函数调用的聊天应用程序*教程中的示例)将其包装成一个演示应用程序。
有关完整代码示例,请参阅食谱。
demo = gr.ChatInterface(
fn=chatbot_with_fc,
examples=[
"Find the top 3 ages with the highest total absenteeism hours, excluding disciplinary failures",
"On which days of the week does the average absenteeism time exceed 4 hours?",
"Who lives in London?",
],
title="Chat with your SQL Database",
)
demo.launch()

总结:用 Haystack 三种方式与 SQL 聊天
在本文中,你学习了几种使用 Haystack 与 SQL 数据库聊天的方法 👇
- 构建一个 Haystack 自定义组件作为 SQL 查询接口,并在管道中使用该组件。
- 通过条件路由跳过无关查询来改进管道。
- 使用函数调用、工具和 Gradio 构建一个完整的文本到 SQL 应用 🚀
感谢你的跟随!
如果你渴望了解更多关于 SQL + LLM 的知识,请查看我们关于*使用生成式 AI 查询大型 BI 表*的文章。

